Investing in the Green Revolution: The Renewable Energy Sector

Solar Power: A Renewable Energy Source
Solar power harnesses the sun's energy, a virtually inexhaustible resource, to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is increasingly important in our quest for sustainable energy solutions, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of traditional power generation methods. The abundance of sunlight available globally makes solar power a potentially significant contributor to global energy needs.
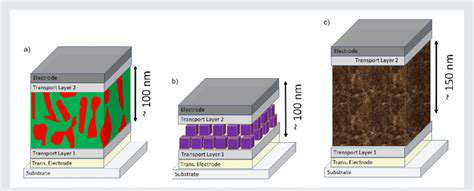
Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This clean and efficient process has seen significant advancements in technology, leading to more affordable and higher-efficiency panels. The decreasing cost of solar technology is making it an increasingly attractive option for homeowners, businesses, and governments.
Technological Advancements in Solar Panels
Significant advancements in photovoltaic (PV) technology have led to more efficient solar panels. These advancements have resulted in a substantial decrease in the cost of solar energy production. Improved materials and manufacturing processes have boosted the efficiency of solar panels, allowing them to capture more sunlight and generate more electricity.
Furthermore, new types of solar panels, such as thin-film solar cells, are being developed to make solar energy more accessible and versatile. These advancements promise to further reduce the cost of solar energy and expand its applications in various sectors.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Power
Solar power offers significant environmental advantages compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power plants. Solar energy production doesn't release harmful greenhouse gases or pollutants into the atmosphere, thus contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment. This cleaner energy source plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and its associated impacts.
Moreover, the reduction in reliance on fossil fuels translates to a decrease in air pollution, which benefits public health, especially in densely populated areas.
Economic Impacts of Solar Power
The solar energy industry is experiencing substantial growth, creating new job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. This expansion in the renewable energy sector has a positive impact on local economies. The creation of new jobs stimulates economic activity and contributes to overall economic growth.
Solar Power Integration into Existing Infrastructure
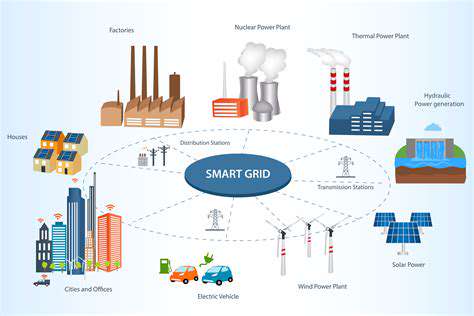
Integrating solar power into existing infrastructure is a crucial step toward widespread adoption. This involves developing smart grids and energy storage solutions to manage the intermittent nature of solar energy. The integration of solar power into existing electrical grids requires careful planning and innovative solutions to address the challenges associated with fluctuating solar energy output.
The Future of Solar Power
The future of solar power looks bright, with ongoing research and development promising even more efficient and cost-effective technologies. The continued decline in the cost of solar energy will make it increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources. This growth will contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy future. Research into new materials and innovative designs will push the boundaries of solar energy technology, enabling even greater energy production and efficiency.
The rise of personalized recommendations is dramatically reshaping how we consume content. Gone are the days of passively scrolling through endless feeds, bombarded by a generic stream of information. AI-powered algorithms are now meticulously analyzing our preferences, past interactions, and even our emotional responses to curate tailored experiences. This shift is not just about efficiency; it's about creating a more engaging and meaningful relationship between consumers and the content they interact with, fostering a more satisfying and relevant user experience.
Beyond Solar and Wind: Exploring Other Renewable Energy Sources
Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, offering a potentially substantial and sustainable energy source. This heat, originating from radioactive decay within the Earth's core, can be harnessed to generate electricity or directly provide heat for various applications. The technology involves drilling wells to access geothermal reservoirs, where steam or hot water is extracted and used to drive turbines or heat exchangers. While geographically limited to areas with suitable geological formations, geothermal power plants can operate reliably 24/7, providing a stable and consistent energy supply, unlike solar or wind power which are dependent on weather conditions.
Significant advancements in geothermal technology are paving the way for more widespread adoption. Improved drilling techniques and enhanced reservoir management strategies are improving efficiency and reducing costs, making geothermal energy a more attractive investment option. Furthermore, the development of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) is expanding the potential of geothermal energy to regions previously deemed unsuitable.
Hydropower: Harnessing the Power of Water
Hydropower, a well-established renewable energy source, leverages the natural flow of water, typically rivers and streams, to generate electricity. This method involves constructing dams to create reservoirs, which store water at a higher elevation. The controlled release of water through turbines spins generators, producing electricity. Hydropower projects can offer substantial energy output and provide valuable flood control and water management benefits, making it a significant player in the renewable energy landscape.
However, large-scale hydropower projects can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat alteration and displacement of communities. Careful planning and environmental assessments are crucial to mitigate these potential drawbacks and ensure sustainable development.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as wood, agricultural residues, and municipal waste, to generate heat or electricity. This process involves converting biomass into a usable fuel source, such as biogas or biofuels, which can then be burned to produce energy. Biomass energy offers a potential solution for utilizing waste materials and can be particularly relevant in regions with abundant agricultural byproducts.
While biomass energy can be a valuable part of a diversified energy portfolio, careful consideration of the environmental impacts is essential. Sustainable biomass practices focus on utilizing waste materials and ensuring that the energy production does not contribute to deforestation or other environmental degradation. Careful monitoring of emissions and responsible sourcing of biomass are critical elements of ensuring its long-term sustainability.
Marine Energy: Tapping Ocean Currents and Waves
The vast ocean holds tremendous energy potential, from the relentless currents to the rhythmic waves. Marine energy technologies are exploring ways to harness this power to generate electricity. Wave energy converters capture the energy of ocean waves, while tidal energy systems utilize the ebb and flow of tides. These technologies are still in the development phase but hold significant promise for expanding our renewable energy options.
The challenges in developing marine energy technologies include the harsh marine environment, high capital costs, and the potential impact on marine ecosystems. Further research and development are necessary to overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of marine energy, but initial results indicate a promising future for this innovative area of renewable energy investment.
Concentrated Solar Power: Focusing Sunlight for Energy
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, generating heat that can be used to produce steam and drive turbines to generate electricity. These systems can operate even at night, storing the heat for later use. While requiring considerable land area, CSP technology offers a significant potential for large-scale energy generation and can play a crucial role in diversifying renewable energy sources.
CSP technology presents economic challenges related to the cost of construction and materials, as well as the need for specialized infrastructure. However, ongoing innovation and research are addressing these issues, making CSP a potentially lucrative and environmentally responsible investment in the future of renewable energy.
The Crucial Role of Sustainable Investments in the Future
Sustainable Investments: A Foundation for a Greener Future
Sustainable investments are not just about environmental responsibility; they represent a fundamental shift in how we approach economic growth. These investments, focused on minimizing environmental impact and maximizing social good, are crucial for building a future that is both prosperous and environmentally sound. By prioritizing businesses and projects that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, we can create a more resilient and equitable world, reducing risks associated with climate change and resource depletion while fostering innovation and economic opportunity.
The long-term benefits of sustainable investments are substantial. From reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy to protecting biodiversity and improving resource efficiency, these initiatives directly address the challenges facing our planet. Furthermore, sustainable practices often lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced brand reputation, making them attractive investments for both ethical and financial reasons.
Driving Economic Growth Through Sustainable Practices
The transition to a sustainable economy is not just about environmental protection; it's a powerful driver of economic growth. Sustainable investments foster innovation in technologies like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture. This innovation creates new jobs and industries, stimulates economic activity, and fosters entrepreneurship. Investing in sustainable practices can also lead to cost savings for businesses, as they become more efficient and reduce their environmental footprint.
Moreover, sustainable investments can unlock opportunities in emerging markets. As developing countries seek to develop their economies, they often face challenges in balancing growth with environmental protection. Sustainable investments can provide the capital and expertise needed to develop infrastructure and industries in a way that minimizes environmental damage and maximizes social benefits, creating a win-win situation for both the environment and local economies.
Attracting Investors and Ensuring Long-Term Value
Sustainable investments are increasingly attracting the interest of investors who recognize the long-term value proposition. Investors are recognizing that environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are no longer just nice to haves but are critical components of long-term financial performance. By integrating ESG considerations into investment strategies, investors can mitigate risks associated with climate change, resource scarcity, and social unrest, while potentially unlocking enhanced returns.
The growing demand for sustainable products and services is also driving the market for sustainable investments. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions, and companies committed to sustainability are often rewarded with increased customer loyalty and brand recognition. This creates a virtuous cycle where sustainable practices are not only good for the planet but also for business profitability and investor returns.