Corporate Renewable Procurement for the Manufacturing Sector: Decarbonizing Operations
Assessing the environmental impact of any activity is crucial for sustainable development. Quantifying this impact allows us to understand the magnitude of the effects and to identify areas where interventions can be most effective. This process necessitates a careful evaluation of various factors, including resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions of pollutants, all of which have significant consequences for ecosystems and human health.
Accurate quantification provides a solid foundation for informed decision-making, enabling businesses, governments, and individuals to adopt more environmentally responsible practices. It also serves as a vital tool for comparing different options and strategies, ultimately fostering a shift towards more sustainable choices.
Types of Environmental Impacts
Environmental impacts are diverse and encompass a wide range of effects on the natural world. These impacts can range from localized effects, such as air pollution in a city, to more widespread and far-reaching consequences, such as deforestation leading to biodiversity loss on a global scale. Understanding the various types of environmental impacts is crucial for effective mitigation strategies.
Several key categories of environmental impacts include changes in air and water quality, habitat loss and fragmentation, biodiversity loss, and climate change. Each of these impacts can have cascading effects on other environmental components, making comprehensive assessment essential.
Methods for Quantifying Impacts
Various methodologies exist for quantifying environmental impacts. These methods often involve employing life cycle assessments (LCAs) to track resource consumption and emissions throughout a product's entire life cycle. This detailed approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of the environmental footprint associated with a product or process.
Other techniques include ecological modeling, which uses mathematical models to simulate the impacts of human activities on ecosystems. These models can provide valuable insights into the potential consequences of different scenarios and help predict future trends.
Data Collection and Analysis
Accurate quantification relies heavily on robust data collection and analysis. Data sources can vary depending on the specific impact being assessed, encompassing everything from government statistics to scientific research studies. Collecting high-quality data is essential for producing reliable and meaningful results.
Data analysis techniques range from simple calculations to complex statistical modeling. Careful consideration of uncertainties and limitations in the data is crucial for producing a nuanced and realistic assessment.
Environmental Regulations and Standards
Governments play a vital role in regulating and setting standards for environmental impact. Regulations often mandate the quantification of specific impacts to ensure compliance and guide businesses towards more sustainable practices. These regulations serve as a critical tool for promoting environmental protection and accountability.
Compliance with these standards can lead to significant improvements in environmental performance, contributing to a healthier planet for future generations.
Economic Considerations
Quantifying environmental impacts often involves assessing the associated economic costs and benefits. These economic considerations can range from the cost of pollution cleanup to the economic value of ecosystem services. Economic valuation tools can help to incorporate environmental factors into decision-making processes.
Furthermore, identifying the economic costs associated with environmental degradation allows for more informed policy decisions that prioritize both environmental protection and economic development.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Examining case studies of successful environmental impact quantification provides valuable insights and lessons learned. These case studies can demonstrate best practices in data collection, analysis, and reporting, ultimately helping organizations to develop their own strategies.
Moreover, sharing successful case studies amongst different industries and sectors fosters knowledge transfer and promotes the adoption of environmentally responsible practices across the board.

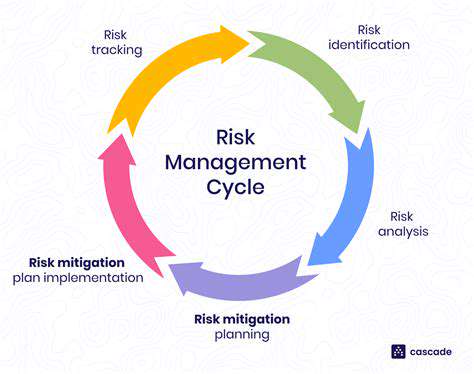
Identifying risk factors is crucial for effective risk management. A thorough understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities is the cornerstone of any successful risk mitigation strategy. This involves not only recognizing the immediate dangers, but also considering the cascading effects that a single event can trigger. Properly evaluating these factors enables organizations to develop proactive strategies and allocate resources effectively.